Introduction to Learning
"Live each day as if it were your last, and learn as you will live forever." Mahatma Gandhi
Just about everyone on planet Earth has been exposed to some type of formal education. Suprisingly, most people don't understand what learning is or how to effectively go about the process of learning. As long as you are a sentient being with a fully functioning anatomically correct brain, you will always learn. Smilkstein (2011) exclaims this fact; "We're Born to Learn." Sounds easy, but can you describe what learning is, how to enact it, how to observe it, how to intentionally evoke it? These questions can all be answered by reading this tutorial which is designed to inform you of what learning is and how to be succesful at it.
 ⇑ Table of Contents
⇑ Table of Contents
Defining Learning
Let's start with the standard dictionary definition of learning: "A persisting change in human performance or performance potential" (Driscoll, 2005, p. 9). "Learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience"
Mayer (2011); Applying the Science of Learning.
By viewing the graphic below you can see that there are three stages to information processing, 1) input, 2) processing, 3) output. In all there are six cognitive processes involved: 1) sensation, taking in information via sensory stimuli, 2) perception, the process of retrieving the sensory information and passing it into short-term memory, 3) attending to the information stored in short-term memory by way of conceptualizing it, synthesizing it, organizing it, using it to solve a problem, integrating it or reteiving related information previously stored in long-term memory, at this point an overt action or performance via the musculoskeletal system occurs or 4) learning it a.k.a. sematically encoding it into long-term memory along with 5) knowing it implicitly or explicitly, and 6) remembering it by retrieving it from long-term memory by way of schema acquisition. From a cognitive perspective, these are the processes of learning.
 Click image for a larger view.
Click image for a larger view.
The Processes of Learning
- Sensation = Reception of input stimuli
- Perception - Recognition of input stimuli
- Learning = Encoding of input information
- Memory = Retrieval of input information
- Thinking = Manipulation of perceived, learned, and remembered information
(Mayer, 1992, p. 8)
"Learning is a change in human disposition or capability that persists over a period of time and is not simply ascribable to processes of growth" (Gagné, 1985, p.2).
Throughout history many of civilization's great thinkers have dedicated much of their lifetime learning how to learn and how to analyze human thinking and how it relates to interactions with their environment in order to answer the question "what is learning?" Defining learning is tricky; there are a lot of theories and even empirically researched studies demonstrating connections between learning events and learning outcomes. The differences when it comes to learning is the theoretical perspective one has about learning. If you are a behaviorist then learning requires an observable outcome. If you are a cognitivist then learning changes knowledge in the learner which can be inferred from behavior (Mayer, 2011). I'm reminded of the old adage "perfect practice makes perfect," this saying says a lot about the bigger picture of learning which some would contend involves cognition, affection, and conation. This definition describes a learning outcome as well as the conditions which need to exist for an optimal learning experience to occur. Hence the use of the modifier perfect with practice instead of just practice. Ultimately, we should critically analyze every thought or situation and apply the best informed behavior toward it each and every time; assessing the consequences and advancing towards a more evolved solution with every attempt. The key to that last statement is that we must apply the "best informed behavior," as these are three important concepts of learning. First, it seems clear that most agree that learning is always an attempt to modify behavior whether done consciously or subconsciously and whether it's done intentionally or not. At some point our mind receives input, records it, evaluates it, and adapts to it. This might be displayed in the form of observable behavior or it might not, but undeniably learning is a physiological adjustment of behavior. Second, the behavior must be informed behavior, meaning one should not just flip a coin to make a decision. This is where experience comes into play. If the experience is a first time encounter with a particular stimulus it must be analyzed to see if it matches up with anything already stored in memory. So being informed is being experienced and knowledgeable about a particular artifact or event. Finally, you need to determine what to do with the input. Theoretically you will make the best decision for you. That is to say that ultimately most people's decisions are influenced by their own self-interest (Smith, A., The Wealth of Nations, 1776). However, for various psychological reasons, you may make a choice that is not best for you, but is best for someone else or some other group of people, plants, or things. You could even make a decision that makes no sense at all; if done so repeatedly the psychological diagnosis would be that you are clinically insane. Decision motivators then fall into one of four categories: self-centered, altruistic, coerced, or insane.
When it comes to learning there is also some debate about the question of nature or nurture. Nature refers to your biological makeup and some argue that you are born the way you are and that your genetic composition will dictate your fate in life. To some extent this is true, your genes will most likely determine your eventual height, the color of your eyes and hair, and whether you will eventually go bald or not. Nurture refers to the environmental influences including that of your parents, your peers, where you live, mass media exposure, even if or where you go to church will sway the way you act and think. These environmental influences won't change the natural color of your eyes or your hair and unless you take up smoking or eat in an unhealthy manner, it most likely won't hinder the height you grow to. A reasonable person should see that neither nature nor nurture exclusively impacts our lives, instead it is a combination of both influences that shape who we are and why we are the way we are. Gagné says "once a person's genetic stock has been chosen at the moment of conception, growth cannot be altered very much, except by extreme measures. But members of human society, which itself is responsible for the care of a developing person, have a tremendous degree of control over events that effect learning" (1985, p. 1).
Essentially, in human beings, learning occurs when the human body receives stimuli physiologically via our senses or chemically by way of the central nervous system as we experience the millisecond by millisecond activities of everyday life. In order for it to be actual learning, the result of processing the stimuli needs to change our behavior. The change some would say must be observable, but others argue that we can learn metacognitively as well and neither a metacognitive process nor it's resultant behavior would necessarily be observable. Another shortcoming of this definition is that it does not indicate that the learning is either beneficial or deep. Which is why learning has been defined by researchers who study learning as stimulus processing which alters behavior in a positive way. This definition of learning is generally how most people think about learning. In this general statement of the meaning there is no mention of education. Education is considered to be induced learning as opposed to experiential learning where you are constantly adapting to the environmental and social interactions around you.
Knowledge
"From an evolutionary perspective, there are two categories of human knowledge: biologically primary and biologically secondary knowledge (Geary, 2007, 2008). Biologically primary knowledge is knowledge we have evolved to acquire over many generations. Examples are general problem-solving techniques, recognizing faces, engaging in social relations, and listening to and speaking our native language. Primary knowledge is modular in that we have independent, cognitive modules that allow us to acquire the relevant knowledge unconsciously, effortlessly, and without external motivation simply by membership in human society. . . Biologically secondary knowledge is culturally dependent. We have evolved to acquire such knowledge in a general sense rather than having evolved to acquire particular knowledge modules such as speaking" (Plass, Moreno, & Brünken, 2010, pp. 29-31).
We are actually learning all the time. Each and every millisecond of every day of your life you are receiving and processing information; most of the time without even realizing it. Thousands of physiological processes are occurring within you as you read this sentence. Most are occurring automatically; partially due to the body's attempt to maintain homeostasis, partially due to routines (habits) you have learned during your lifetime to the point of automaticity, and possibly a few processes you actually gave thought to. I'm guessing you didn't have much trouble reading and comprehending the previous sentence in less than only a few seconds. This would mean that most likely you didn't have to read each letter, or symbol if you will, individually to recognize and recall its meaning and context from memory in just milliseconds of time.
In general, cognitive psychologists profess learning to be a physiological modification to the brain. In theoretical terms it is a schema modification in long-term memory. To a neuroscientists this would mean adding, changing, or pruning neural pathways in the brain. It really depends on the point of view that you are coming from. The behaviorist camp would describe behavior as an observable change in behavior. Mayer (2011) writes that "learning is a change in knowledge attributable to experience" (p. 14).
⇑ Table of Contents
Lifelong Learning
⇑ Table of Contents
Learning How to Learn
⇑ Table of Contents
Learning Strategies
- Basic Rehearsal Strategies
- Repeating the names of items in an ordered list like the order of the planets in the solar system
- Complex Rehearsal Strategies
- Used when the to be learned material is prose, such as a lesson from a science textbook
- Repeating the material aloud (i.e., shadowing)
- Copying the material
- Taking verbatim notes
- Underlining important parts of the material
- Basic Elaboration Strategies
- Explain concepts you are learning to others
- Complex Elaboration Strategies
- Prepare presentations for your peers
- Tutor your peers about a subject
- Basic Organizational Strategies
- Order concepts into a tree structure or org chart
- Complex Organizational Strategies
- Identify how how concepts are related to one another and prioritize those relationships
- Organize a lesson plan for how to instruct others about a subject
- Comprehension Monitoring Strategies
- Applying metacognitive analysis on how well you are learning and retaining detailed information about a subject
- Affective and Motivational Strategies
⇑ Table of Contents
Neuroscience
Parts of the Brain
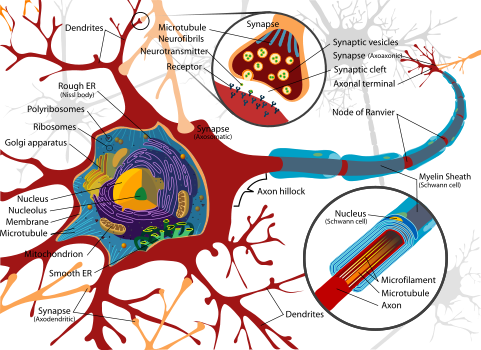
Neurons
Neurons transmit nerve impulses in the brain. A human brain is made up of an estimated 15 - 33 billion of these nerve cells. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons.
A neuron is comprised of three parts:
- The soma (The cell body)
- The axon, which carries signals from the soma to the presynaptic ending.
- The dendrites, which carry signals from the postsynaptic ending to the soma.
Notice the Myelin sheathing which coats the synapses that connect the neurons in the brain. The Mylelin sheathing helps the conductivity of the Synapse between the neurons. The more times a neuron is accessed the thicker the Myelin sheathing is on the Synapse meaning the neural pathway becomes stronger and more easily accesed. This is why repetition is a good learning strategy, because it helps strengthen the neural pathways for retreiving the stored information.
⇑ Table of Contents
Learning Styles - An Educational Myth
I am continually amazed how the myth of learning styles continues to be perpetuated by so-called teachers and school administrators who supposedly have masters and PhD degrees in education. I compiled these links here so that instead of trying to argue with these folks, I can simply email or text them the URL for this page to help educate them to the fact that learning style claims like "I'm a visual learner" or "I learn better hands-on" are actually claims without empirical merit and are actually some of the biggest educational myths there are.
YouTube Videos on the Learning Styles Myth
Literature Review on the Learning Styles Myth
⇑ Table of Contents
Learning Links of Interest
Knowledge Retention: Effective Strategies To Supercharge Your Memory - This Web page from Growth Engineering presents effective strategies which will help you increase memory retention and offers a link for downloading a PDF version of 100 Brain Science Tips to Boost Your Training Strategy. Author: Growth Engineering: Hary Cloke
The Science of Thinking - How the brain works, how we learn, and why we sometimes make stupid mistakes.
Submit ideas: http://ve42.co/GotIdeas
Apply to work with me: http://ve42.co/JoinUs
Thanks to Patreon supporters:
Nathan Hansen, Donal Botkin, Tony Fadell, Zach Mueller, Ron Neal
Support Veritasium on Patreon: http://bit.ly/VePatreon
This video was inspired by the book Thinking Fast and Slow by Daniel Kahneman
Harpist: Lara Somogyi http://ve42.co/Lara
Animator: Jesse Agar http://ve42.co/ThisPlace
Filmed by Raquel Nuno
Music by Kevin MacLeod, http://incompetech.com "Sneaky Adventure" "Harlequin" Author: Veritasium
- Length: 0:12:09
Study Skills & Evidence-Based Learning Strategies - Evidence-based strategies for teaching and learning is a video designed for both teachers and students to help close the achievement gap and increase test scores. These specific strategies have been researched and used by a number of students and teachers as a classroom practices and as part of a lesson. Now, not all strategies are going to work for every student or every lesson, but watching the entire video will give you an overall understanding of different ways to increase learning and enhance neurological well-being. This video is part of a playlist from teachings in education to help educators throughout their teaching career. Author:
Teachings in Education
- Length: 0:06:29
Elon Musk’s 2 Rules For Learning Anything Faster - A structure to help you take over entire industries. Author: The Art of Improvement
- Length: 0:06:24
The Most Persistent Myth - Many technologies have promised to revolutionize education, but so far none has. With that in mind, what could revolutionize education?
These ideas have been percolating since I wrote my PhD in physics education: https://ve42.co/phd
I have also discussed this topic with CGP Grey, whose view of the future of education differs significantly from mine: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7vsCA...
I think it is instructive that each new technology has appeared to be so transformative. You can imagine, for example, that motion pictures must have seemed like a revolutionary learning technology. After all they did revolutionize entertainment, yet failed to make significant inroads into the classroom. TV and video seem like a cheaper, scaled back film, but they too failed to live up to expectations. Now there is a glut of information and video on the internet so should we expect it to revolutionize education?
My view is that it won't, for two reasons: 1. Technology is not inherently superior, animations over static graphics, videoed presentations over live lectures etc. and 2. Learning is inherently a social activity, motivated and encouraged by interactions with others.
Filmed and edited by Pierce Cook
Supported by Screen Australia's Skip Ahead program.
Music By Kevin MacLeod, www.incompetech.com "The Builder" and by Amarante Music: http://www.amarantemusic.com Author: Veritasium
- Length: 0:07:22
Learning from dirty jobs - Mike Rowe the host of "Dirty Jobs," tells some compelling (and horrifying) real-life job stories. Listen for his insights and observations about the nature of hard work, and how its been unjustifiably degraded in society today. Author: Mike Rowe
- Length: 0:20:02
Elon Musk: The Scientist Behind the CEO (and How He Teaches Himself) Documentary - This mini documentary takes a look at how Elon Musk sees the world through a scientific and engineering mind - and how this fuels the businesses he has started. We will also take a look at how he taught himself about different industries: from banking (Paypal), to rocket engineering (SpaceX). Elon Musk champions the use of physics as a way of thinking. And believes that more people should be innovating in manufacturing - to help build the city of the future. Rather than entering the finance, law, or internet based industries. This video also takes a look at the 'reasoning from first principles' framework - which will allow anyone to view their world, personal and business, just like Elon. Author: Venture City
- Length: 0:16:34
How to Study Effectively for School or College [Top 6 Science-Based Study Skills] - How to study effectively with 6 essential skills. Boost your study performance with strategies recommended by science - The ANSWER Method. These tips are for high school or university students preparing for exams or wanting to learn more effectively. This video is a collaboration between The Learning Scientists (http://www.learningscientists.org/) and Memorize Academy (https://www.memorize.academy). Author: Memorize Academy
- Length: 0:08:27
⇑ Table of Contents